Understanding Blue Light Skin Damage and How to Prevent It
What Is Blue Light?
Blue light (400–490 nm) penetrates deeply into the dermis—farther than UVB—and disrupts skin health at a cellular level. It triggers oxidative stress, damages collagen, and can stimulate melanin production, contributing to hyperpigmentation and uneven skin tone. Unlike sunburns, the effects of blue light on skin are not immediately visible but can accelerate photoaging when exposure is frequent and unprotected.
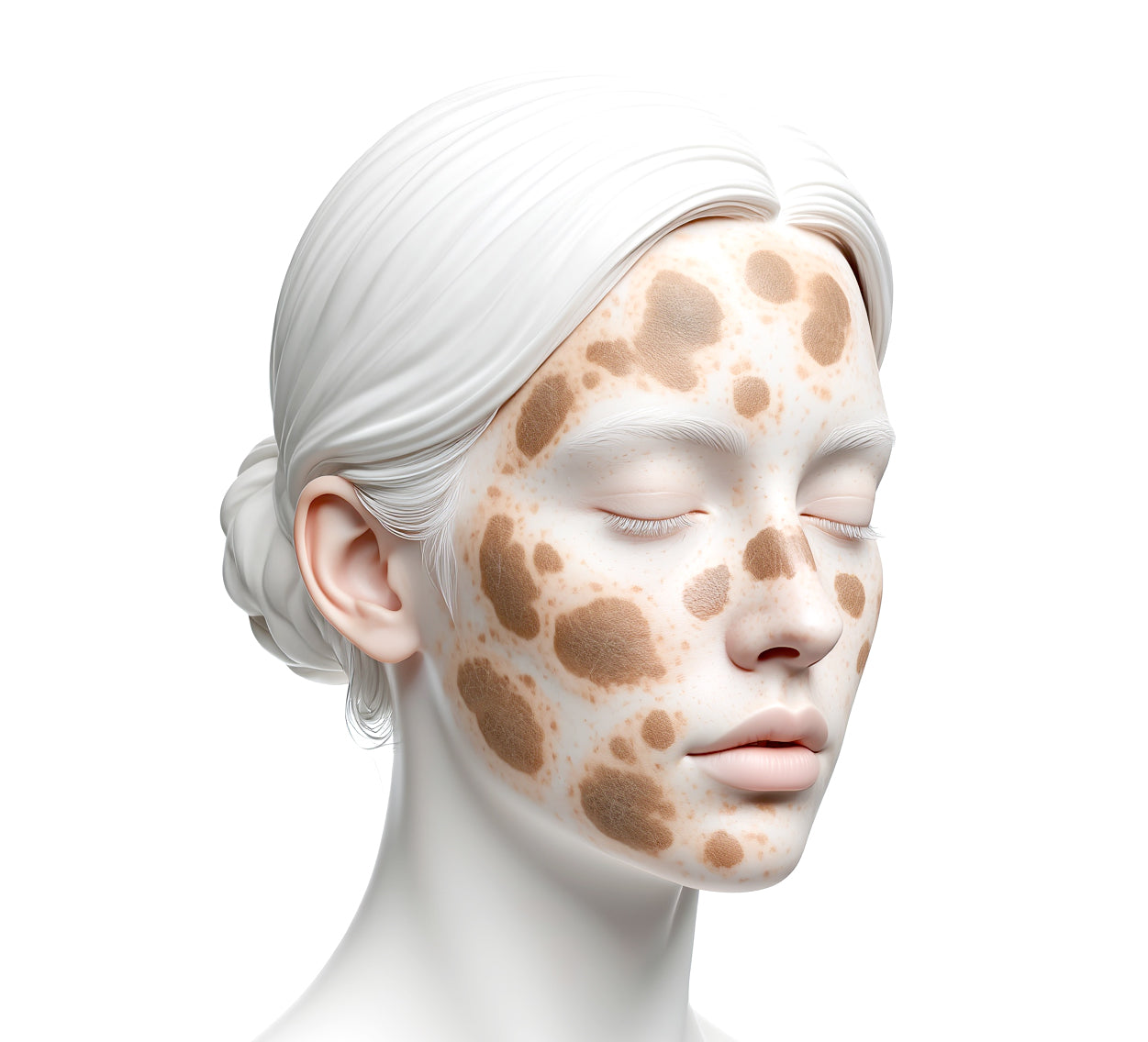
Signs of Blue Light-Induced Skin Stress
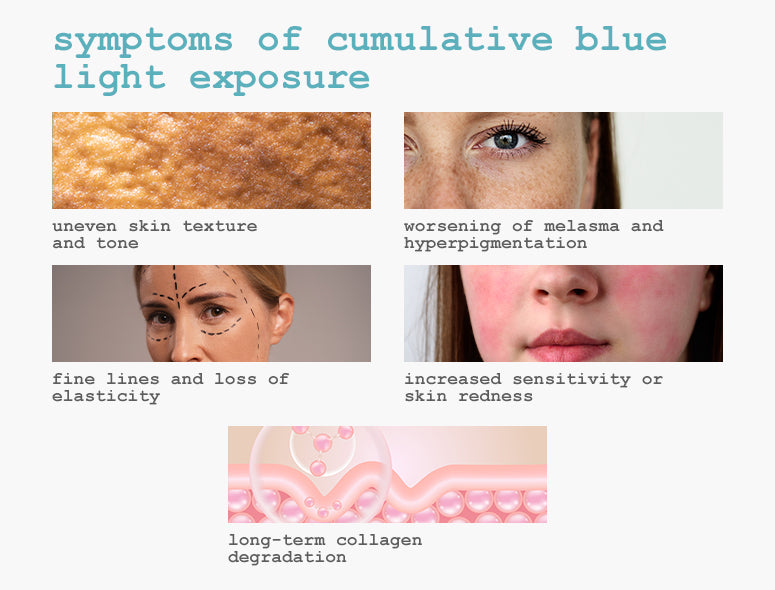
Symptoms of cumulative blue light exposure include:
- Uneven skin texture and tone
- Worsening of melasma and hyperpigmentation
- Fine lines and loss of elasticity
- Increased sensitivity or skin redness
- Long-term collagen degradation
For many, these changes are subtle yet persistent, especially in those with pigmentation-prone or sensitive skin.

Common Sources of Blue Light
- Sunlight (the largest source of HEV light)
- Smartphone, laptop, and tablet screens
- LED lighting and fluorescent bulbs
- TVs and digital advertising boards
How to Prevent and Treat Blue Light Damage
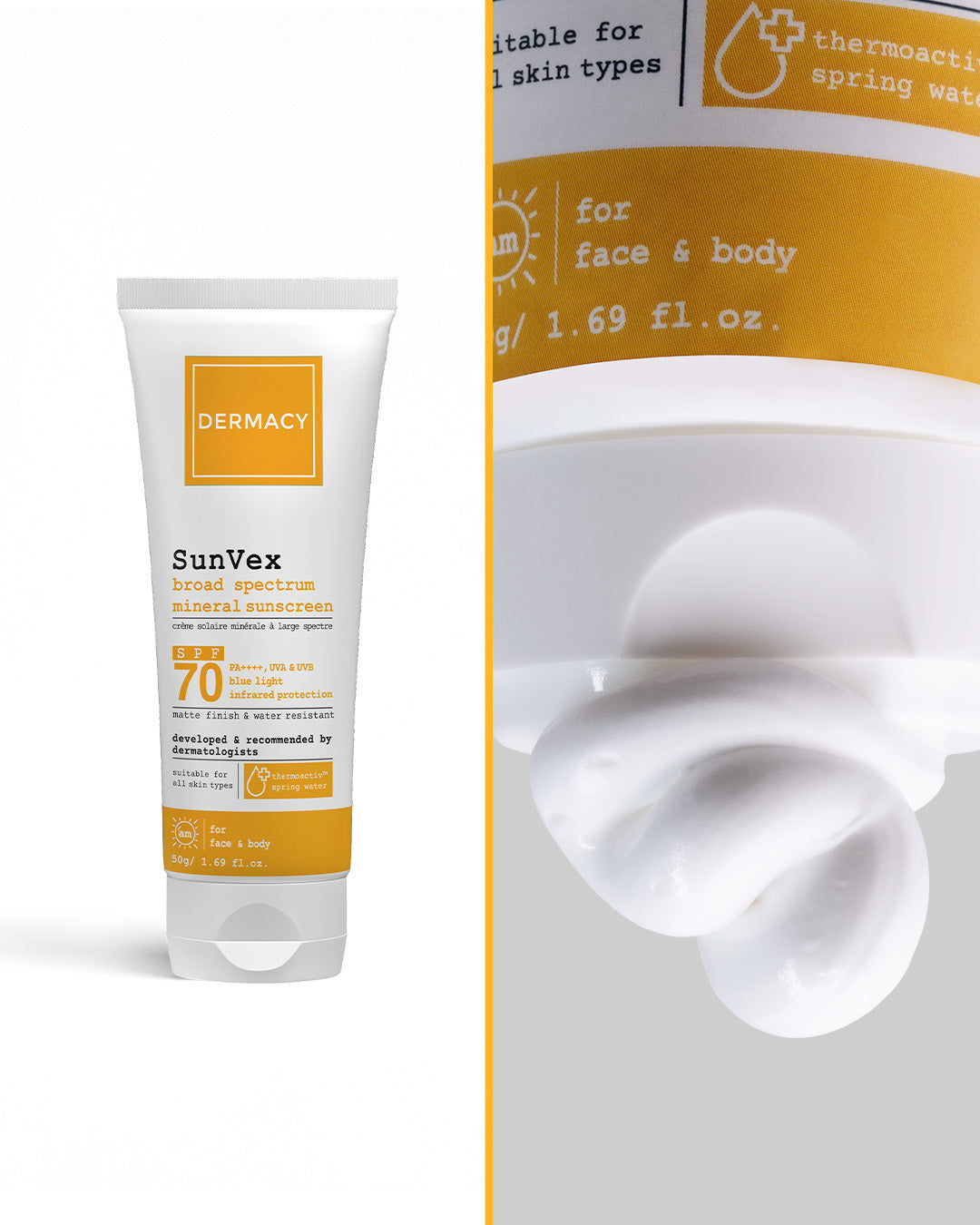
1. Use a Blue Light Sunscreen Daily
Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with HEV defense. The best blue light sunscreens often include iron oxides, encapsulated UV filters, or mineral SPF formulas. These block both UVA/UVB rays and visible light wavelengths.
2. Incorporate Antioxidants for Skin Protection
Daily use of antioxidant cleansers and antioxidant moisturisers can counteract free radical damage. Ingredients like vitamin C, niacinamide, and resveratrol are proven to protect the skin from blue light effects.
3. Reinforce the Skin Barrier
Moisturizing creams with ceramides, squalane, and glycerin prevent dehydration and shield skin from blue light-induced oxidative damage.
4. Limit Direct Exposure
Use screen filters and lower screen brightness. Opt for blue light mode on devices, especially during nighttime.
5. Commit to Nighttime Repair
Use barrier-repair creams and antioxidant serums to reverse the daily stress caused by blue light exposure.
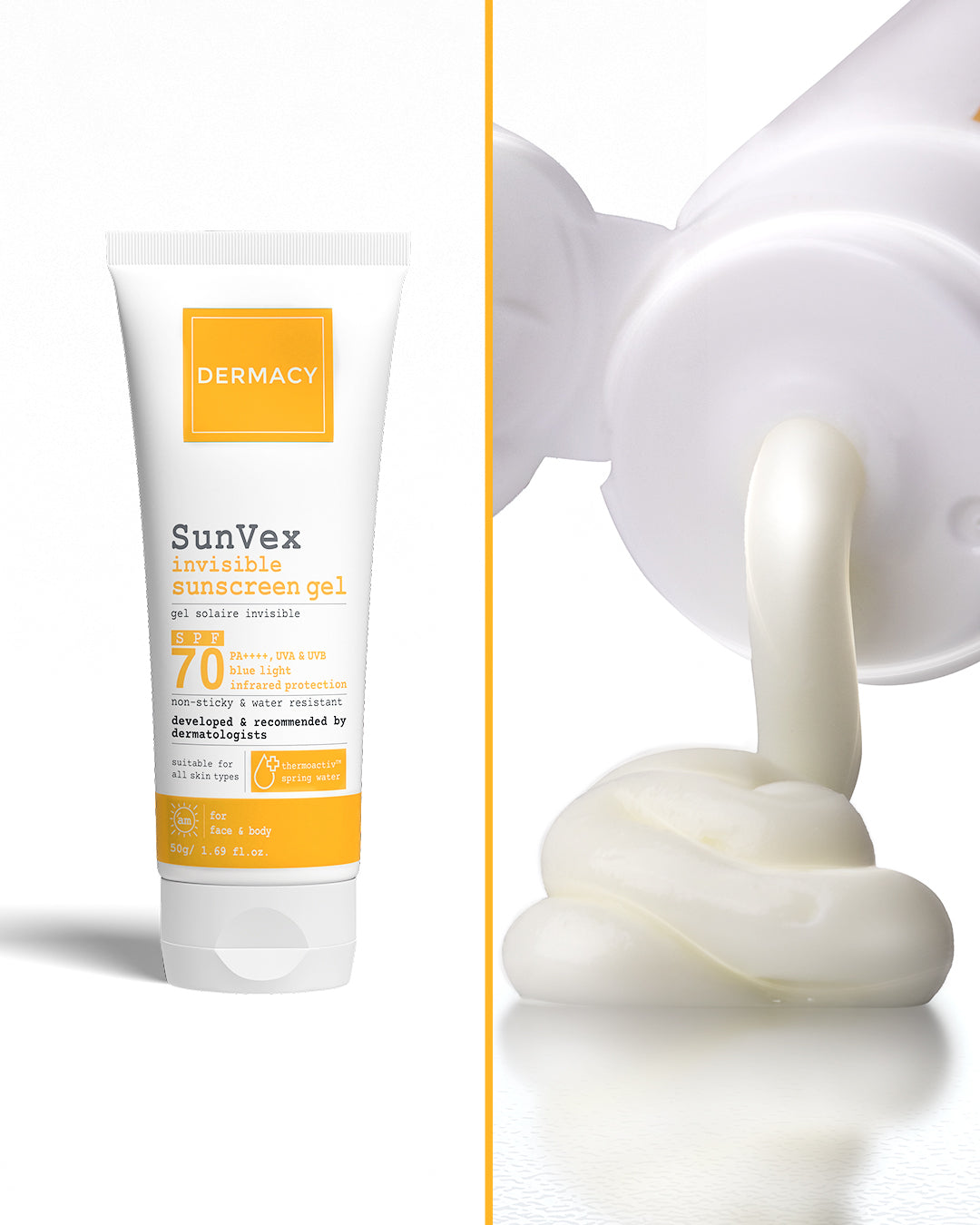
Dermat Recommends
The Dermacy SunVex Range offers a dermatologist-formulated approach to blue light skin treatment:
- Encapsulated UV filters and iron oxides for comprehensive UVA, UVB, and blue light protection
- Thermal Spring Water and Centella Asiatica to reduce inflammation and support skin recovery
- Lightweight, non-comedogenic textures that work for daily use, even on sensitive or acne-prone skin
Final Takeaways
Blue light damage may not be visible immediately, but its long-term effects on pigmentation, barrier function, and aging are real. Incorporating antioxidants for skin and blue light sunscreen into your routine is essential for anyone exposed to screens or artificial light throughout the day.
In today’s digital age, where exposure is nearly constant, protecting your skin from the effects of blue light is just as important as guarding against UV rays.